
TL;DR: Timely email delivery is critical. Delays in transactional or marketing emails can result in missed opportunities and reduced customer trust. Utilize monitoring methods such as timestamp analysis and round-trip tracking to ensure emails reach inboxes within seconds.
Table of Contents:
How Email Delivery Works
Timely Email Delivery Importance?
4 Signs That Your Emails Are Not Reaching Customers on Time
Common Causes of Delays in Email Delivery?
How to Measure If Emails Are Reaching Customers on Time
How to Optimize Email Delivery Time
Conclusion
FAQ
Imagine sending a password reset link or a payment confirmation email to a customer.
How quickly should it land in their inbox?
Within seconds. Right?
Any delay can frustrate the customer or make them question the brand's credibility.
So, how can you ensure your emails actually reach customers in time?
This article explains how email delivery works, why email timing is important, four signs of late emails, what causes delays, and how to measure and optimize email delivery time.
How Email Delivery Works
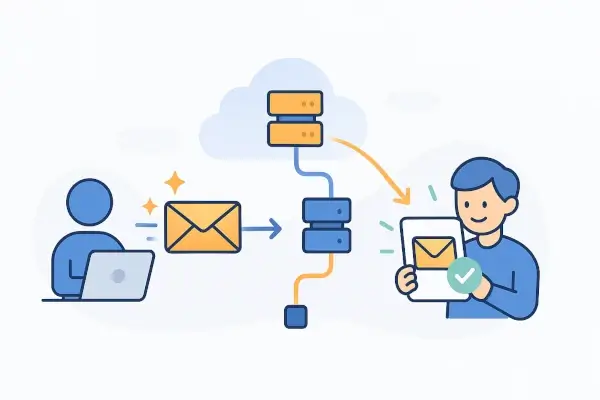
Before going straight to the importance of email delivery, let's first understand the email delivery flow:
Step 1: Design and Send Email
The sender drafts and finalizes the email on a platform, then clicks the send button to deliver it to the intended recipient.
Step 2: Link to SMTP Server
Using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), the email client establishes a connection with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server, like Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, etc.
Step 3: Format and Authenticate the Email
SMTP formats the email in Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) format and authenticates using the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) protocols.
Step 4: Set Email in Queue and Forward
The system routes the authenticated email to an outgoing queue and forwards it to the recipient's address.
Step 5: Email Processing at Recipient's Server
The recipient's server validates the sender's email based on the address, subject line, or content and decides whether to accept, reject, or delay the email.
Step 6: Email Delivery to the Inbox or Spam
Once the recipient's server accepts the email, it delivers the message to the receiver's inbox or spam folder, depending on the email validation.
Why Is Timely Email Delivery Important?
Most companies track email delivery to ensure that emails don't bounce but reach the recipients.
However, successful delivery doesn't guarantee that emails arrive at the right time.
For example, if you launch an email campaign for a flash sale but your messages reach customers after the sale is nearly over, the campaign loses its purpose.
This also applies to time-sensitive deals in fast-moving business models like print-on-demand, where customer satisfaction largely depends on order confirmation emails arriving on schedule.
Similarly, if you send service notifications about scheduled maintenance but customers receive them after the maintenance is over, they may experience issues without any warning.
Delays like these can lead to missed opportunities, reduced customer trust, and lower engagement.
4 Signs That Your Emails Are Not Reaching Customers on Time
The following are the four common signs that reflect delays in email deliveries and require immediate attention:
- A sudden decline in the email open rate indicates that your emails are either arriving late after the best time to send the emails or are landing in the spam folder.
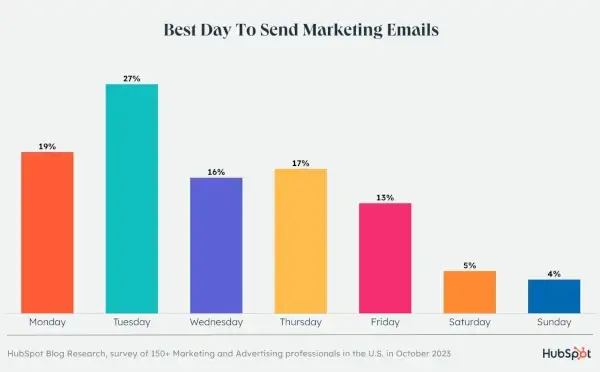
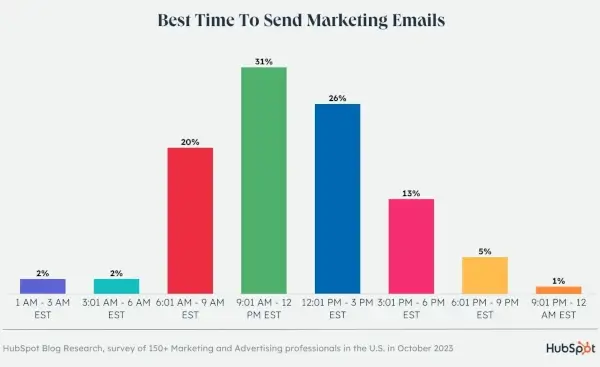
According to HubSpot, Tuesday is the best day, and 9:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. is the best time to send emails to customers.
- You start receiving customer feedback and emails regarding delays in receiving your emails. This may point to issues with the server or routing.
- You observe an increase in the bounce rate, and your emails are not reaching the desired inbox.
Here's how you can calculate the email bounce rate:
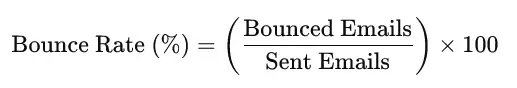
- Transactional emails, such as payment and login detail links, or order confirmation emails, may arrive late at the recipient's server, even after a triggered action.
What are the Common Causes of Delays in Email Delivery?
Here are the four main reasons why email delivery may be delayed:
1. Bad IP Reputation
When your IP address has a poor standing or appears on an email blacklist, mail servers might hold up your emails, causing delays or rejecting your messages.
Performing email blacklist monitoring can detect these issues fast. This process involves checking your domain against major blacklists like Spamhaus, SpamCop, and Barracuda.
2. Greylisting
Some mail servers use greylisting to temporarily reject emails that appear suspicious or spam-like. Using IPWhois.io, you can detect potential threats by revealing information about the IP address of the email and determining if an IP address is associated with malicious activity, such as spam, phishing, or malware distribution.
This method can cause repeated sending delays until the sender tries again after some time.
As a consequence, genuine emails may arrive considerably later than expected.
3. ISP Throttling
Internet service providers (ISPs) often slow down emails by limiting the number of messages they allow from one sender within a specific time frame, as they're busy.
This slowdown puts email in line, resulting in delivery delays.
4. Problems With DNS Settings
Incorrect setups for SPF, DKIM, or Domain-Based Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) can cause receiving servers to block or reject emails.
Popular email lookup tools like Clay, Hunter.io, and Snov.io can help verify domain settings.
How to Measure If Emails Are Reaching Customers on Time
Simply finding out whether your email reached the customer or bounced back does not give you enough insight.
Email deliverability is only a part of the equation. If you aren't reaching your customers within seconds, you are losing opportunities and trust. Real-time monitoring is no longer optional; it is crucial to customer experience and business performance.
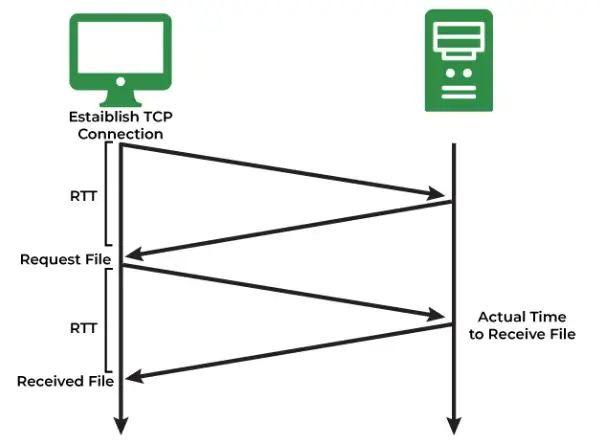
Email Round-Trip Monitoring
Email round-trip monitoring thoroughly measures the time it takes for an email to move from the sender to the receiver and also back as a response, if any.
To successfully perform this exercise, it establishes test inboxes at several email providers like Gmail and Outlook.
The system then sends test emails at specific intervals, monitors the delivery time, and records any observed delays.
This method helps teams identify delays, pinpoint the location of the delay (SMTP server, POP3, or IMAP services), and continuously monitor email performance in real-time.
Here's how the email round-trip monitoring process flows:
Timestamp Analysis
To determine whether your emails reach customers on time, track and analyze the email delivery timestamps.
These timestamps indicate the exact time when your email service provider verified the message and when the recipient's mail server accepted it.
The timestamp data may also indicate that the receiver successfully received your email, but it does not confirm whether the email was delivered to the inbox or another folder.
Measure SMTP Response Time
It calculates the time it takes the receiver's mail server to respond to your SMTP delivery request.
An immediate response may indicate a successful in-time delivery of the sender's email.
However, if it takes a longer response time, then there is probably throttling at the server or some other issue causing a delay.
To evaluate SMTP response time, go through the server logs or use diagnostic tools like Postmaster by Google, SMTPdiag tool by Microsoft, or Wireshark offered by the respective email service provider (ESP).
Use Read Receipts and Pixel Tracking
Read receipts can provide valuable insights into how quickly emails reach your customers.
When a receiver opens an email having a read receipt or tracking pixel enabled, you may receive a notification regarding the precise time of engagement with the receiver.
Furthermore, you can analyze the timestamps to determine when you sent the email and when the recipient opened it.
This helps detect delivery delays and the receiver's inactivity.
How to Optimize Email Delivery Time
Now that you understand how to determine whether your emails are reaching recipients on time, let's explore how you can optimize email delivery time:
Continuous Process Monitoring
Implement tools and metrics to monitor email time, performance, and response continuously.
You can adopt strategies like email round-trip monitoring (as discussed in the previous section) to measure the time it takes for an email to reach the recipient and receive a response from the sender, including the time spent traversing internet service providers (ISPs).
Setting up monitoring regularly will allow you to analyze email delivery performance over time, identify variations or slowdowns, and determine how efficiently your email service provider delivers emails.
Enable Blacklist Monitoring
Being blacklisted can significantly reduce your email performance and severely damage your brand reputation.
The following image displays how an email ends up on a blacklist:
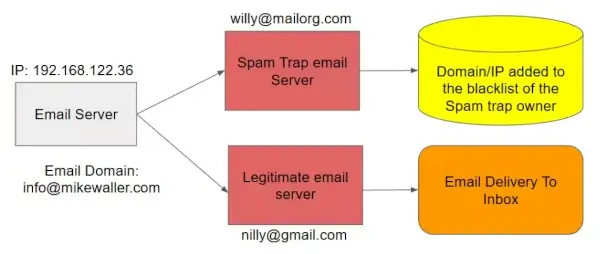
Servers can delay or reject your email, so it's crucial to enable email blacklist/DNSBL monitoring when sending emails to customers.
Also, follow email best practices during your marketing efforts and take prompt, correct, and effective actions to remove your domain from blacklists, in case you get listed.
Authenticate Your Emails
To ensure timely email delivery, you must authenticate your emails by correctly setting up DNS records.
Configure SPF to set which email servers can share emails on your behalf, add DKIM to attach digital signatures to add authenticity to your emails, and enable DMARC to notify recipient servers on how to manage unauthenticated email communications.
This approach can boost a sender's reputation and minimize delays caused by spam filters.
Test Before You Send
Create engaging email content, and before emailing your list or sharing emails with real customers, send test emails to a seed list of email addresses.
You can use various email service providers, such as Google, Outlook, Yahoo, etc.
Constantly monitor the test email to determine when it reaches the recipient's server, and identify the cause of any delays in email delivery.
Measure email deliverability to identify whether your test email lands in the spam box or directly in the inbox of the customer.
Here's how to calculate email deliverability:
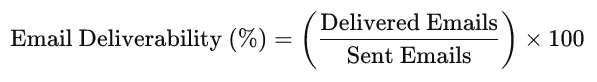
Start Ensuring Timely Email Deliveries
One out of every six emails fails to reach the customer's inbox.
This might happen due to delivery delays caused by spam filters or because the recipient's server rejects the email, flagging it as blacklisted or originating from a suspicious domain.
In a competitive marketing landscape, even a minor delay in your marketing email may result in loss of leads or revenue and damage to the brand's trust.
Therefore, ensure that your emails arrive on time and in the correct mailbox. Don't. Don't just observe whether they are delivered.
Looking to monitor your email marketing services?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is timely email delivery, and why does it matter?
Timely email delivery means that emails, especially transactional or time-sensitive ones, reach the recipient's inbox within seconds of being sent. Delays can lead to missed opportunities, frustrated users, and reduced trust in your brand.
2. How long should it take for an email to arrive?
Ideally, emails, especially those related to password resets, order confirmations, or alerts, should be delivered within a few seconds to a minute. Anything longer may be considered a delay, especially if triggered by a user action.
3. What are the common signs that my emails are being delayed?
- Drop in open rates
- Customer complaints about late emails
- Higher bounce rates
- Transactional emails arriving well after a user action
4. What causes email delivery delays?
Common causes include:
- Poor IP reputation (e.g., blacklisted sender)
- Greylisting by receiving mail servers
- ISP throttling due to sending limits
- DNS misconfigurations (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
5. How can I check if emails are reaching users on time?
You can use:
- Round-trip monitoring (send-and-receive tests)
- Timestamp analysis (when sent vs. received)
- SMTP response time checks
- Tracking pixels or read receipts
6. Does successful delivery mean the email arrived on time?
No. An email can be marked as "delivered" even if it arrived late. Delivery confirmation only means the server has accepted it, not that the recipient has seen it quickly or at all.
7. How do I improve email delivery time?
- Monitor delivery performance continuously.
- Set up proper email authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
- Avoid blacklists by maintaining good sending practices
- Test emails before launching a campaign
8. Can I measure email deliverability and bounce rate?
Yes.
- Bounce Rate = (Bounced Emails / Sent Emails) × 100
- Deliverability = (Delivered Emails / Sent Emails) × 100
These metrics help evaluate email performance and identify delivery issues.


 Copyright 2000-2026, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.
Copyright 2000-2026, WebSitePulse. All rights reserved.